Ticks and Tickborne Disease
Ticks are small arachnids, related to spiders, that feed on the blood of mammals, birds, reptiles, and amphibians. While their bites are often painless, certain species can transmit a variety of pathogens (bacteria, viruses, and parasites) that cause serious illnesses in humans and animals, known as tickborne diseases.

Tick bite prevention can include avoiding tick habitats when possible, using U.S. Environmental Protection Agency-approved insect repellants, like DEET, when outdoors, showering immediately after returning indoors, performing tick checks, and removing ticks promptly.
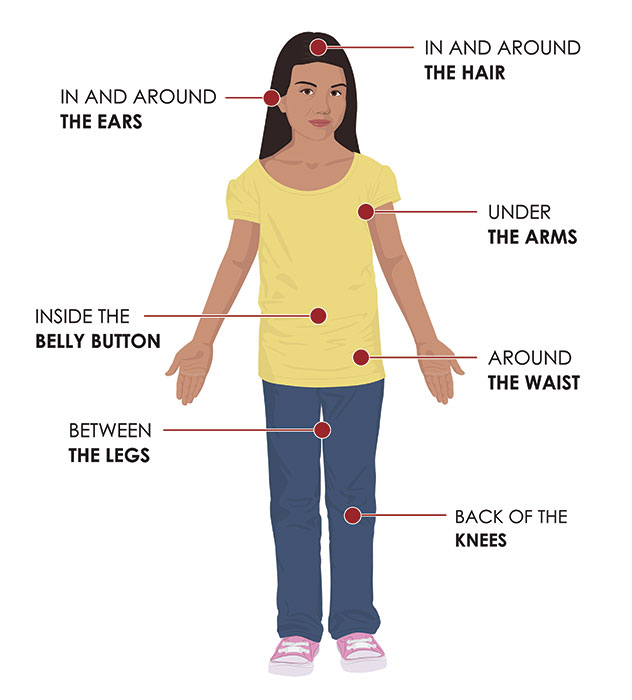
When performing tick checks, people should pay special attention to under the arms, in and around the ears, inside belly button, backs of knees, in and around hair, between the legs, and around the waist. People with pets should do the same for their indoor/outdoor pets, so they are also less susceptible to tickborne disease and less likely to carry ticks into their family’s yard and hom
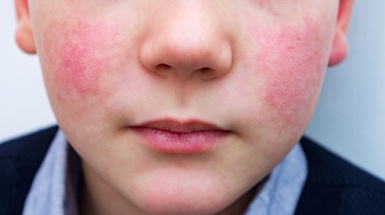
According to the Ohio Department of Health (ODH), many tickborne diseases can have similar signs and symptoms.The most common symptoms of tick-related illnesses are:
- Fever/chills: With all tickborne diseases, patients can experience fever at varying degrees and time of onset.
- Aches and pains: Tickborne disease symptoms include headache, fatigue, and muscle aches. With Lyme disease, patients may also experience joint pain. The severity and time of onset of these symptoms can depend on the disease and the patient's personal tolerance level.
- Rash: Lyme disease, southern tick-associated rash illness (STARI), Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF), ehrlichiosis, and tularemia can result in distinctive rashes.
Physicians are also encouraged to help their patients by increasing their awareness of Lyme disease and other tickborne diseases and educating them on preventive actions to avoid the disease before they experience symptoms.
For more information about ticks and preventing the diseases ticks may transmit, visit https://odh.ohio.gov/know-our-programs/zoonotic-disease-program/diseases/tickborne-diseases. CHD has educational brochures and tick identification kits available to residents and physicians. Call 513-357-7391 for more information.
CHD Communicable Disease Dashboard:
(See page 4 for Lyme disease data.)
Additional Resources from the CDC:
- Understanding tick bites and Lyme disease (PDF)
- Información sobre las picaduras de garrapatas y la enfermedad de Lyme (PDF)
- Tick removal
- Eliminación de garrapatas y pruebas
- Tick Bite Bot -This tool guides you through the proper steps for removing attached ticks and helps you decide if and when you should seek medical attention after a tick bite.
- CDC: Diseases Transmitted by Ticks-A Lists of known pathogens spread by ticks.
- CDC: What to Do After a Tick Bite-A selection of resources showing life cycles, proper tick removal, bite prevention, illustrations of how to do a proper tick check and more.
Tickborne Prevention Videos
Revised 07/22/2025
Latest News
-

- Jun. 13
- Bats and Rabies